When it came to on-page SEO techniques, there was a period when keyword stuffing was the norm. With Google’s Panda update, websites that used this approach were pushed to the bottom of the search results!
Strategies that work today in SEO may not function in a few years. This is why I always advise aspiring SEO marketers to stay on top of what’s going on in the field.
The Search Engine Results Page (SERP) listing has been replaced by pages that provide value to users in the post-Panda era. If you want to rank a page on Google, your first objective should be to add value to the material that currently ranks in the top spot.
The two most important elements that Google considers when ranking websites are on-page and off-page variables, as you may know (link building). This blog will show you both fundamental and complex on-page optimization techniques that you may apply to your page.
So, let’s start with the fundamentals of on-page SEO actions. Please use the table of contents section to explore and begin reading if you’re looking for advanced tactics.
What is On-page SEO?

On-Page SEO is a website optimization approach that helps search engines rank pages within a website. On-page SEO ensures that a page ranks higher in search engines for relevant terms, resulting in focused visitors.
On-page SEO tactics include content optimization, URL optimization, metadata optimization, image optimization, and page speed optimization. On-page SEO, as the name implies, is concerned with improving the internal parts of your website in order to make it more search engine friendly.
Websites that do not perform on-page optimization frequently do not appear on the first page of search results. The reason for this is that while ranking pages on the first page, the Google Algorithm takes into account a few on-page characteristics.
Relevance is one of the most important variables in determining a page’s SERP position. You won’t rank on Google 99 percent of the time if the information on your page isn’t relevant to the query entered.
Ensure that the page remains relevant to the intended audience at each stage of on-page optimization. Your page will have a high bounce rate if it is not relevant to the users, and it will eventually lose its place in the Google results.
Is On-Page SEO a Ranking Factor?
The relevancy of the results delivered to users is critical to the success of search engines. Google is currently omnipotent in the search landscape because, according to its superior algorithms, it offers the best results to users.
As a result, on-page optimization becomes even more critical. The goal of on-page SEO is to guarantee that both users and search engines comprehend what a website has to offer.
This also presents an opportunity, because efficient on-page SEO operations open the road for you to locate your target audience and effectively communicate with them. All of the elements you’ll learn about in this piece are crucial since they provide essential signals to search engines about your website.
If you skip any on-page SEO steps, your competition may take your place in the SERP, which is exactly what you don’t want.
ALSO READ: What Are Breadcrumbs & How To Use Them For Effective SEO
On-page SEO Techniques
As you may be aware, on-page SEO activities are one of the most important SEO ranking elements, and they have the power to make or destroy your website.
Here are a few basic On-page SEO elements that can have an impact on a page’s search engine rankings.

Optimize Content
You’ve probably heard the SEO adage, “Content is King.” As I mentioned in the outset, the SEO sector is quite dynamic, and things change all the time. Although content is still a deciding element, the quality of the content is determined by a variety of criteria.
You may have encountered situations where your high-quality content does not appear on the first page of Google’s search results. The main reason for this is because the text was prepared without much consideration for the target audience.

If you publish long-form material on a topic that isn’t relevant to your target audience, despite your best efforts, you’re unlikely to obtain organic traffic. What you need to do as an SEO is figure out what your target’s most often asked questions are and try to answer them with your content.
Proper keyword research will assist you in identifying the most commonly searched query string, which you can then incorporate into your content to help you rank higher in search engines. Learn how to uncover keywords that will get you to the top of Google Search by reading our in-depth article on how to do keyword research.
Furthermore, the ideal plan is to figure out what kind of material is effective for your competition and replicate it on your own website. Emulating, on the other hand, does not imply duplicating or scraping content.
Google despises websites that do this, and things can quickly spiral out of control if you engage in such behaviour. The best method to achieve this is to find competitor material and adapt it to your own unique perspective by adding more information, facts, and research.
Optimize URL Structure
The URL is the element that SEOs place the least emphasis on. You can’t disregard the URL, though, because it’s the most basic component of a website.
Furthermore, all of the crucial considerations regarding internal links, site layout, and link juice, which we’ll explore later in this blog, revolve around the URL.
You may have seen URL constructions like this before:
You can tell it’s a complete disaster just by looking at it. The issue with these URLs is that neither users nor search engines can decipher what is included within the link.
A URL is designed to give users and search engines a general idea of what the page is about. This is one of the reasons why I usually advise making URLs as short as feasible while incorporating the desired keyword.
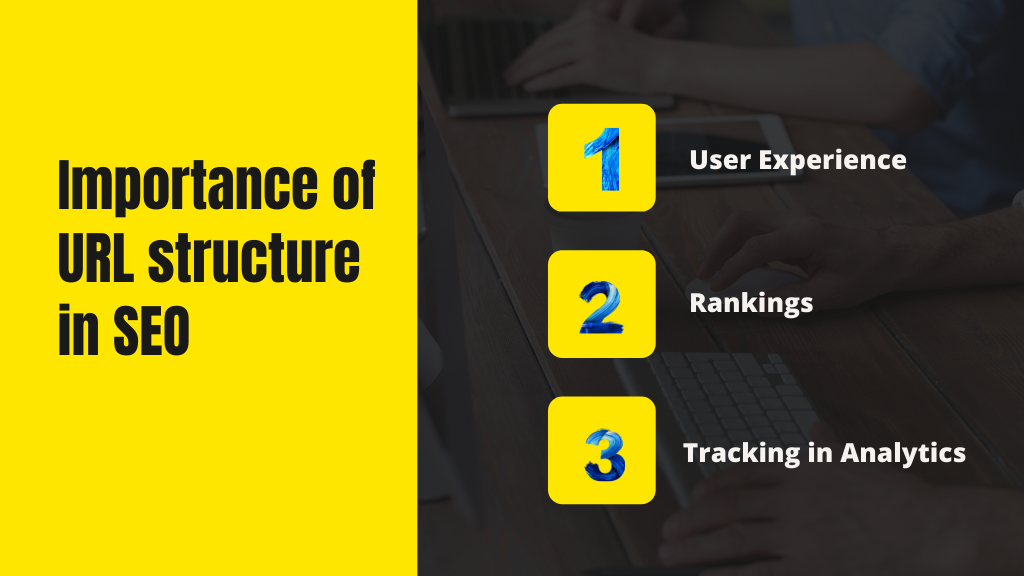
The following is an example of a good search engine and a user-friendly URL:
Go to Google and type in “iPhone 11 Pro.”
The top ten results all have clear URLs, as you can see.
If you use WordPress, Joomla, or another CMS for that purpose, the title tag is used to automatically construct SEO-friendly URLs. The URLs, on the other hand, tend to be longer if the title is long. The ideal approach is to put the target keyword at the start of the URL and leave the rest out.
If the target term has previously been used on another website, create the URL using the secondary or LSI keywords.
Optimize Meta Tags
The meta title and description of a page must be optimized in order to improve the website’s search engine rankings and click-through rate.
How Important is a Good Meta Description?
Although Google has clarified that meta description is not a ranking element for SEO, disregarding it might result in valuable click-through rates being lost.
The ideal strategy to optimise a website’s meta description is to provide users with compelling reasons to visit the page. Google will most likely display the language that enters into the meta description on SERPs (unless it decides not to and picks up some random description from the content).
Because you’re up against at least ten other people, it’s critical to make the description as click-worthy as possible. You don’t have to load the description with keywords to make it click-worthy. If you believe it will provide more value, use the keywords and LSI as organically as possible.
However, this may not assist you improve your Google SERP rank.
How to Optimize Meta Title Text?
The meta title is still an essential on-page ranking element after all these years. The finest meta title optimization tip is to make sure your goal term appears first in the title.
Here’s an example of how I improved the meta title of my top-ranking page after the Google Algorithm Update. My target keyword is “Google Algorithm Update,” which I have intentionally placed at the start of the title after a semicolon.
I change the title, description, and content whenever there is a new update. The initial half of the meta title, however, stays unchanged. This method works well for long-form material as well as content that will be evergreen.
When it comes to meta title optimization, one of the most typical mistakes SEOs do is placing the target term near the end of the title.
This method may backfire because Google may shorten the keyword when displaying it on the SERP. It lowers the chances of the page showing up and being clicked.
Optimize Heading Tags
Both search engines and people may get a good indication of what they’re reading by looking at the heading tags on a page. The H1 tag appears to be an essential ranking element for crawlers, particularly Google’s.
Including the target term in the H1, which is typically the page title, has the same ranking impact as optimising the Meta Title. If there is no predefined Meta title, Google will most likely examine the H1 element of a page.
The use of numerous H1 tags is widely misunderstood. Multiple H1 tags, on the other hand, will not harm a page’s search engine rankings, according to Google’s John Mueller. He also stated that several H1s are acceptable to Google’s algorithms if the users are satisfied with the content’s structure.
Using the many permutations of the heading tag, on the other hand, would undoubtedly supply Google with adequate information about the primary subjects and subtopics. Because featured snippets are chosen based on the sub-topics given beneath each article, this can add more value.
Optimize Images for SEO
When reading the content that you have written and published, web surfers are tremendously distracted nowadays. People’s attention spans have shrunk significantly, and boring text is one of the reasons they tend to shift their focus.
Images, unlike other resources like video or music, are consumed on-the-go, making them one of the most powerful tools in digital marketing and communication.
Furthermore, there’s a good chance you’ll be able to get more organic traffic from Google Image Search. For SEO pros, however, optimising pictures for search engines is one of the most important organic SEO tactics for increasing a website’s organic presence.
Importance of Optimizing Images for Search Engines
One of the most common errors made by webmasters is failing to optimise photos for search engines. While most SEOs optimise other components of on-page SEO, such as title, description, and so on, image optimization is still regarded technical on-page SEO, and it is left to the designer or developer to do.
If you want to rank first on Google, you can’t neglect images. Consider a site with high-quality content and high-quality backlinks.
The pages on the site have every reason to rank, but if one of them contains an image that doesn’t meet image optimization criteria, it will have a negative impact on the website’s overall ranking, wasting optimization efforts.
If you used to believe that simply changing the Alt text of your images could help you rank higher on Google, then this guide will be a revelation for you.
You’ll be shocked to learn about the numerous ways to optimize photos and find solutions to some of the critical difficulties that are dragging your website down in the rankings after reading the recommendations we’re about to share.
About <img> Tag
<img> tags are self closing tags within HTML. This tag, unlike the other HTML tags such as <a> tag, doesn’t have to be closed separately as it closes itself.
Example for Open & Close Tag:
<a href=”” title=””> </a>
Example for Self-closing Tag:
<img src=”” alt=”” title=”” />
How to Select Images?
Use photos that are closely related to the subject, depending on the content you’re presenting on the website. Real people, objects, and products, for example, are some of the most widely utilised photos.
Use photos that are closely related to the subject, depending on the content you’re presenting on the website. Real people, objects, and products, for example, are some of the most widely utilised photos.
What is the Recommended Image Size?
The size of your images is largely determined by the platform/CMS you’re using for your website. For example, if you’re using WordPress, the most recommended image size is 1024 580 pixels. The default width is 1024 pixels if you follow the BoostStrap standards. The height, on the other hand, may vary based on the other requirements.
When it comes to image file size, images that are smaller than 50 KB are strongly recommended. According to the Google LightHouse tool, an image should be 30KB in size. The reduced file size is one of the reasons why JPG photos are recommended. File sizes for other image kinds, such as ClipArt (PNG), Vector (SVG), and GIF, are typically larger.
A website’s picture sizes are usually predetermined. Users can, however, upload higher-resolution photographs, which slows down the process again. Ideally, the images should be prepared after talking with the developer about the exact size needed.
For instance, if the website only requires a 9090 pixel image, provide the precise file size rather than 90120 or any other number. This forces the developer to use more CSS to adapt the image, which can slow down the website.
How to Optimize Your Alt Text?
The image alt text is a crucial on-page SEO component that many website owners overlook. The alt text of a website image is usually a description of the image.
When an image fails to load on a page, this comes in helpful for web browsers. In certain circumstances, the alt description text will fill the image space and provide context for users. Aside from that, a written copy that appears on a webpage in place of an image if the picture fails to load on the user’s screen.
Apart from that, search engines appreciate Alt text for assisting the visually handicapped in understanding the material, hence it plays a vital role in On-page optimization. However, currently, SEOs try to cram keywords into the alt text, which defeats the purpose.
The ideal strategy here is to include a detailed alt text that includes the LSI keywords so that the user can understand what the image is about.
ALSO READ: Alt Text for SEO: Image SEO in 2021
How to Optimize Image File Name for SEO?
An crucial aspect of optimization is christening an image. The name of the image should be related to the main topic of the page. This is one of the most straightforward ways to tell Google that the image is highly related to the content.
This is also an excellent time to highlight your secondary or LSI keywords. Ensure that the space between each word is replaced with a hyphen when optimising the image file name.
This will prevent using WordPress or other CMS platforms by using the percent 20 instead of the space in file names.
Example:
https://www.example.com/img/on%20page%20optimization.jpg is incorrect.
https://www.example.com/img/on-page-optimization.jpg is correct.
After taking a screenshot or downloading an image from Shutterstock or Pixabay, some webmasters forget to alter the file name. This isn’t the greatest practice because the file name doesn’t correspond to the page’s content.
It’s also a good idea to avoid using unusual characters and symbols in the file name, as this makes it difficult for Google to understand the concept and rank your image.
How to Optimize Image Title for SEO?
The optimization of picture title tags is something that many SEOs and website owners overlook. The title tags, on the other hand, serve a significant role in assisting visitors in identifying the picture name.
When viewers hover over an image, the title tags are usually displayed. The tooltip hover effect may influence usability, hence most webmasters omit adding title attributes to images.
Keywords are not allowed to be crammed into title tags. They are the image’s representation and must be in a format that Search Engine Bots can interpret.
How to Optimize the Image Caption for SEO?
The third and most overlooked image property is the caption. The caption, on the other hand, plays a crucial function in giving users a quick overview of the image it portrays.
Captions are used most effectively on news websites. If you have an image that depicts an action, event, or feeling, captions might assist users learn more about it.
The caption is frequently used by website owners to include copyright information or to credit the image to its original source. Adding a descriptive caption is a highly-recommended on-page SEO strategy as the search engine bots read captions as content within the page.
Proper Internal Linking

As the owner of a website, you should establish a hierarchy to each area. Users and search engines will be able to simply access and retrieve relevant information as a result of this.
Internal links are links that take you from one page of the website to another. Text, photos, videos, and documents can all be used to create the link.
The prominence of pages within a website is determined by the internal linking structure.
As Google transmits link juice, it’s critical to understand the importance of each page. Only a properly interlinked website may pass link juice generated on one page to the next, hence the concept of link juice applies to internal links as well.
Consider the following advanced internal connection factors:
Crawl Depth:
When building a website, crawl depth is an important internal linking component to consider. The internal linking architecture of a website impacts how easy a search engine can find and index pages, which is referred to as crawl depth.
In general, a crawl depth of three is the limit, as any deeper pages may fail to capture the interest of the crawler during the initial crawl.
For increased crawlability, important money pages (service, product pages) should be strategically positioned within the crawl depth region of 0-2 pixels.
Page Hierarchy
Internal linking is one method of establishing a website’s page hierarchy. The higher the internal link value you offer a page, the more important it is to Google.
Link Relevancy
Even though the links are contained within your website, this does not imply that any page can be linked to another. Because Google dislikes websites that try to fool its algorithm, only relevant pages should be linked.
Use highly relevant anchor language to offer internal links to contextually relevant pages.
Contextual Links
Adding an excessive number of links to a page is considered a negative SEO technique. Including 100 internal links in a 1000-word article will make the page appear spammy, and Google may not display it on the first page.
Even though there is no set quantity for internal links, it is critical that they remain natural.
Anchor Text
Anchor Texts are useful for linking between pages inside a website. It is the anchor text that provides Google Crawlers with contextual information about the relationship between the pages.
Long-tailed anchors are preferred for internal linking since they provide more context to users and Google crawlers.
Remove Intrusive Interstitial Properties
Consider a website that displays a full-screen video ad and then redirects you to another page with many pop-ups when you close it. Instead of closing the pop-up, I would exit the entire tab and proceed to a less complicated page to complete my search.
This is a common blunder made by websites, which results in a reduction in organic reach. It’s vital to provide users with a consistent web experience if you want to stay at the top of Google’s search results.
Google has began penalising websites that use an excessive number of interstitial properties on their pages. Google announced in 2016 that any website attempting to impose invasive interstitial advertising would be penalised.
Check for Keyword Density
One of the most fundamental On-page SEO variables is keyword density. Those days of keyword stuffing, on the other hand, will not get you to the top of the search results now.
Google’s algorithms are now programmed to detect and penalise websites that stuff keywords. Keyword density has evolved under these new circumstances, and it now has more to do with advanced on-page SEO tactics like LSI and TF/IDF.
Using the same keywords over and over again can only harm your SEO approach. Making Google comprehend that the words used within your content are contextual and pertinent to the broader issue is the way of the future.
If you use the target keyword three to four times in your content in 2020, it will still rank if you used the LSI and TF/IDF techniques.
What are LSI keywords? How to use LSI keywords?
LSI Keywords, also known as Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords, is a Google approach for determining the relationship between words on a page and the topic being discussed. LSI Keywords are words that appear in a topic and are contextually relevant. To evaluate the quality of the material, Google utilises its algorithm to locate and interpret the common phrases that exist on multiple websites for the same topic.
With LSI keywords in place, Google can now identify the quality of the material despite the fact that the keyword appears less times in the text.
The best technique to identify LSI keywords is to use Google search’s “Related Search” feature, as well as some free LSI tools.
TF-IDF: Can It Really Help Your SEO?
The acronym TFIDF stands for Term Frequency–Inverse Document Frequency. Google’s John Mueller was the first to certify that the company’s search engine retrieves data using the TFIDF method.
TFIDF is an information retrieval approach that attempts to determine the significance of a group of words on a page in relation to the overall index of all web material.
TFIDF is simply one of several measures used by Google in its information retrieval strategies. Furthermore, because the TFIDF statistic is based on an aggregation of all the information currently indexed by Google, optimising a web page based on it is difficult.
However, you may evaluate whether your content qualifies for the fundamental TFIDF measure using tools like SEMRush Writing Assistant or TFIDF Tool.
Schema Markup/Structured Data
Google SERP Features are now proving to be major drivers of Click Through Rate. The majority of these SERP characteristics are due to websites using Structured Data or Schema Markup.
Structured Data is information that websites supply to search engines in order for them to better interpret the content. Structured Data guarantees that search engines deliver useful information/hints to users even before they access a web page.
The reviews that appear in search results for Movies, Events, and Products are the best example of Structured Data assisting people. Structured Data is not a ranking element for SEO, according to Google. Missing out on Structured Data, on the other hand, may result in lower click-through rates.
Due to the lack of extra information, your target audience may go for your competitors instead.
Going back to the beginnings of Structured Data, it was an initiative launched in 2011 by the search engine market’s behemoths – Google, Bing, and Yahoo – to make it easier to grasp the intent of each page.
There is a lot of information on the internet that hasn’t been categorised or structured.
The search companies sought to simplify web content, so they created a coding standard to aid their algorithms in picking up information quickly and efficiently.
When structured data is enabled on a website or on specific pages, search engines will crawl the site and show rich information or rich snippets.
MUST READ: How to Submit URL to Google for indexing?
What are the Structured Data Formats?
JSON-LD
This is the Google-recommended Structured Data format, which makes use of JavaScript notations or markups on a page to help search engines figure out what kind of page it is.
Microdata
Microdata is another another format for describing structured data. Despite the fact that this is a Google-approved Structured Data Format, it is prone to causing code errors because it is injected directly into the HTML.
It’s a time-consuming approach because it uses inline coding to style the page’s real elements, slowing down the page.
RDFa:
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) is an HTML5 addition that uses tags inline with current HTML, comparable to Microdata. RDFa is a markup language that is used to markup metadata on a webpage.
Sitemap.xml File
Crawlers for search engines are busily indexing millions of pages on the internet. The amount of time they spend on each website is determined by a variety of factors, including the number of pages, the speed with which the site loads, and the HTTP status codes.
Having said that, enabling a sitemap will enable them in crawling your site’s pages more quickly. A sitemap is an XML file that is placed on a website to assist search engines in navigating between pages.
Sitemaps are simple to create, and there are a few programmes available to assist you, such as the free Sitemap Generator Tool.
If you manage a CMS-based website, however, the process is significantly easier because sitemaps are usually included as a standard feature.
You must add the sitemap to the Google Search Console in order for Google to index the pages within it.
One of the most significant benefits of a sitemap is that it informs Google crawlers about the relevance of each page. The crawler can tell which page is more significant because a sitemap is built based on page hierarchy.
A sitemap also gives information on the content’s freshness, which aids the crawler in reindexing pages.
Here to how to submit sitemap to Google Search Console.
Robots.txt File
A sitemap is just as necessary as a robot.txt file. Almost all websites have a robots.txt file to prevent a few pages from being indexed by search engines.
It will not harm your SEO efforts if you don’t have a robot.txt file. They may, however, take away your crawl budget because search engine bots may spent time crawling and indexing pages that aren’t relevant to your users.
Look for https://www.yoursite.com/robots.txt on your site to see if you’ve implemented Robot.txt.
You can check it here, how to submit sitemap on Google Search Console.
Optimize Page Speed
There has been a lot of talk regarding the page of a website since Google revealed that the load speed of a website is one of the criteria for organic ranking. Google Page Speed Insights is a useful tool for SEOs to check a page’s loading speed.
There has been a lot of talk regarding the page of a website since Google revealed that the load speed of a website is one of the criteria for organic ranking. Google Page Speed Insights is a useful tool for SEOs to check a page’s loading speed.
The Page Speed Insights tool considers a number of aspects when determining site speed, and it all starts with the web hosting service you choose.
Modern customers have less patience and are overwhelmed by the number of options available to them. They like to look at websites that load quickly. So, what is the ideal time for a page to load? In a blog post titled Google Recommended Page Load Time, we go over this in detail.
The best technique to speed up website loading is to shrink the size of a few on-page elements like JavaScript, CSS, and images.
These elements consume a significant portion of the page load time, and optimising them can reduce your website’s page load speed.
Adapting to current frameworks like Angular JS and React can also improve the speed of your website. Sites that deliver a consistent user experience are always given a boost by Google. Keeping your website free of technical on-page SEO concerns will help you improve your organic rankings.
Here is how to do website speed optimization in 2021.
Increase E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness)
Google has been very explicit about penalising websites that lack E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). The E-A-T acronym comes from the Google Quality Rater Guidelines.
Despite the fact that the early editions of the quality rater standards said little about E-A-T, the subsequent versions had an entire section dedicated to the notion.
Google considers a number of criteria before deciding on a page’s fate on its results page, and E-A-T is now one of them, especially if you’re dealing with a YMYL site.
YMYL sites have the potential to affect end-users’ lives and security. Google has recently been more cautious about how website content can damage consumers’ livelihoods.
As a result, E-A-T was created, which analyses whether the information on the site is real and valid. This is especially true for websites related to health, banking, finance, and wellness, all of which fall within the YMYL umbrella.
The E-A-T score of a website is determined by a number of variables, including the niche (alternative medicine websites have a difficult time ranking on Google), the Author Bio, About Us, Security Features, Policies, and so on.
I’ve produced an in-depth guide on how to optimise each of the E.A.T elements described above so that your website ranks higher than your competition.
What are Some On-Page SEO Mistakes?
Do you have outstanding content that isn’t ranking? In this essay, we’ll go through eight onsite SEO pitfalls to avoid.
If you want your web pages to appear in the Google search engine’s top results, you must have a basic understanding of on-page SEO tactics. Many people lack sufficient SEO understanding, and as a result, they frequently struggle with technical on-page SEO.
Over the last two decades, the landscape of digital marketing has changed dramatically. Google’s algorithm changes on a regular basis, causing companies to lose SEO methods and content marketing strategies. As Digital Marketers, you’ve invested time and effort into determining which strategies and practises will perform best for your company.
However, you should be aware that blunders can cause your website’s ranking to drop unintentionally. Let’s have a look at what these blunders are.

Duplicate Content
If you have duplicate content on your pages, you’re making one of the most common onsite SEO blunders. Because there are so many businesses like yours, each one is attempting to create distinctive content that will help them establish authority in a specific sector.
If you want to stand out from the crowd, you must provide unique, high-quality material on a regular basis. When adding filters to a category or product listing, one common duplicate content problem occurs. Using the “canonical tag” will help you avoid this blunder. This reduces the possibility of Google discovering duplicate pages and avoids one of the most common on-page SEO errors.
Forgetting the Importance of Keyword Research in On-Page SEO
You can’t learn about your target audience unless you undertake proper keyword research. Keywords serve as a link between the user’s purpose and the material. As a result, make sure that your content is keyword-optimized.
Your content will never rank on search engines if it has a broad topic but is not optimised for the keywords that your target audience searches for on the internet.
This is due to the fact that appropriate page optimization with highly relevant keywords will help your web pages rank higher in search engines. Furthermore, it would allow your blog to generate leads.
When it comes to blogging, you should concentrate on long-tail keywords, or keyword phrases that provide useful information, which are sometimes referred to as informational keywords.
Some bloggers do not optimise their headers, meta tags, or text for the keyword phrases that readers are looking for, while others over-optimize their content. Both of these are poor on-page SEO practises.
Keyword stuffing and over-optimization of material might make your content appear spammy to Google. As a result, be sure to naturally incorporate targeted keywords into your content to help it rank higher in Google SERPs.
No Sitemap
What is a sitemap, exactly? An XML file is used to create a sitemap. XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language, and it’s a format for storing and transporting data.
Sitemaps provide crucial information to search engines about a website’s most important pages, such as the date the page was last updated. “The emphasis here is on the most crucial pages,” says Karl Kangur, founder of Business Media. You have serious structural concerns if you need a sitemap only to get Google to properly crawl your site.
You’ll want to make sure your sitemap (and Google index) only includes pages that bring value to your website. Do a Google search for your website with the phrase “site:mydomain.com,” look through all of the results, and ask yourself, “Is this something someone would want Google to land on?” If the answer is no, these pages should not be indexed and removed from your sitemap. Keep the authority for your most important pages.
This enables the spider to intelligently crawl through the webpage. True, building a sitemap does not guarantee a search engine’s success, but it does make crawling easier for the bots. Indirectly, a higher crawl rate can help with better ranks.
No Header Tags
The content is frequently structured using header tags. These tags also aid search engines in determining which parts of a page are more significant.
The content of the page is prioritised using header tags. However, if you utilise it incorrectly, it might be perplexing.
To prevent making this onsite SEO mistake, make sure the primary header tag is unique and that all essential keywords are included on the page. Those keywords can also be used in appropriate subheadings.
No Image Description and Alt Tags
There’s also the fact that photos aren’t understood by search engines. As a result, the required Alt text must be included as part of the image description.
The image would be easier for search engines to grasp with such a phrase. One of the onsite SEO blunders you can be making is including an imprecise description in the photos. To get better results, try to avoid it.
Poor Meta Tags
Even before people visit your website, Meta Descriptions give them a sense of what’s on offer. A solid meta description, on the other hand, is critical for increasing organic Click Through Rate.
True, the Meta description isn’t used as a ranking criteria for on-page SEO. According to previous study, roughly 30% of websites use duplicate meta descriptions, while approximately 25% of websites do not use meta descriptions at all.
Make sure that each page on your website has its own meta description.
Broken Links
Broken links on your site could be one of the most serious onsite SEO blunders! You’ll need to update your resources as your site grows. It’s not a big deal if one or two links are broken. You can immediately fix it by properly setting up 404 pages or sending users to an appropriate page on your website using 301 redirects.
It could be problematic, however, if there are a lot of broken links. There could be numerous reasons for this, such as the visitor seeing the 404 pages rather than the essential information. It causes a significant decline in organic traffic. Furthermore, your website would be seen as of poor quality.
You’re probably wondering how you can tell whether a link is broken. You can use various Site Audit tools such as SEMrush or add plugins to check the links in your content to find broken links.
Slow Load Times
The loading times of a website were included in Google’s algorithm, which was announced in 2018. If your websites take a long time to load on both desktops and mobile phones, it can affect your website’s ranking.
You can simply analyse the loading speed of your website with Google’s PageSpeed Insight tool. Not only that, but it also explains why your website is taking so long to load and how to fix it.
Some of the common remedies include removing render-blocking JavaScript, allowing CSS compression and minification, and optimising HTML. The extra spaces are deleted, and the loading speed is increased automatically.
Conclusion
I believe I’ve offered enough ammunition to dispel the myth that on-page SEO is simply a matter of adding a few more keywords to sites. This guide will be updated when I discover new on-page SEO tactics for improving website rankings in search engines. Please let me know if you think I missed something important in this on-page seo checklist in the comments area.
10 Essential On-Page SEO Factors You Need to Know
Learn what on-page SEO is, why it’s vital, and 10 of the most crucial on-page SEO factors you should pay attention to in order to succeed.
To be successful in organic search today, you must optimize for a variety of characteristics that search engines value, including technical, on-page, and off-page variables.

Off-page approaches, such as link building, and other technical features have received more attention in recent years. Off-page SEO, on the other hand, won’t help you much if you don’t pay attention to the basics — on-page SEO.
On-page optimization should always be a top priority for smart SEO practitioners. Because the search landscape is constantly changing, it’s critical to keep your on-page SEO skills up to current. We’ll go through what on-page SEO is, why it’s vital, and 10 of the most critical on-page SEO factors today in this piece.
What Is On-Page SEO?

On-page SEO (sometimes referred to as on-site SEO) is the process of optimizing web pages in order to increase a website’s search engine ranks and generate organic traffic.
On-page SEO comprises optimising your headlines, HTML elements (title, meta, and header), and images in addition to posting relevant, high-quality content.
It also entails ensuring that your website possesses a high level of competence, authority, and credibility.
It considers a variety of factors on a webpage that, when combined, will boost your website’s visibility in search results.
Why On-Page SEO Is Important
On-page SEO is crucial because it aids search engines in comprehending your website and its content, as well as determining whether it is relevant to a searcher’s query.
In search engine results pages, relevancy and semantics are becoming increasingly important as search engines get more sophisticated (SERPs).
With its variety of complex algorithms, Google is now far better at:
- Understanding what users are looking for when they type in a search query.
- Providing search results that are relevant to the user’s search query (informational, shopping, navigational).
- Adapting to this change is critical, and you can do so by making sure that your website and its content – both what is visible to users on your webpages (text, images, video, or audio) and elements that are only visible to search engines (HTML tags, structured data) – are well-optimized according to the latest best practises.
Furthermore, you can’t just disregard on-page SEO because you have more control over on-site factors than you have with off-page SEO, which relies on external signals (i.e., backlinks).
You’ll observe an increase in traffic and a rise in your search presence if you put work into on-page methods.
This guide will take you through the most critical on-page SEO factors.
Focusing on these ten areas can help you boost your content and authority, as well as your rankings, traffic, and conversions.
E-A-T
Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-A-T) is the framework that Google raters use to evaluate content providers, webpages, and entire websites.
High-quality content has long been a priority for Google. It wants to ensure that sites that provide high-quality content are rewarded with higher ranks, while low-quality content sites are penalized.
There is a direct link between what Google regards to be high-quality content and what appears in search results.
Whatever you want to call it — correlation or causation – E-A-T is influencing Google’s organic search results in some way. As a result, E-A-T must be factored into your SEO approach.
Title Tag

The title tag, which is an HTML tag found in the head section of each webpage, serves as an initial cue or context for the topical subject matter of the page it is on.
ALSO READ: What is Title Tag & Best Practices of Writing Title Tags
It is prominently displayed in both the search engine results pages (usually as a clickable link) and the browser window.
Because the title tag has little impact on organic rankings on its own, it is frequently neglected.
However, title tags that are missing, duplicated, or badly written can all have a detrimental impact on your SEO results, so make sure you’re optimising for it.
Meta Description

Meta descriptions have been an important optimization factor since the beginning of SEO. Meta descriptions, or meta tags that describe what a page is about, are frequently displayed in the SERPs beneath the page title.
ALSO READ: How to Write a Compelling Meta Description
While Google claims that meta descriptions have no bearing on results, anecdotal evidence suggests that indirect benefits of better descriptions do. Correctly optimising the meta description can help you:
- Rate of click-through (CTR).
- Perception of the result’s quality.
- All of your visitors’ perceptions of what your website has to offer shift.
Headlines
Do you want your website’s content to rank well in search engines? Then begin crafting catchy headlines.
It may seem simple to come up with a title for a blog article, but a good headline can mean the difference between a click and an impression, which is why it’s critical to do so strategically.
To stand out in the SERPs, your headlines must pique visitors’ curiosity, entice them to click through and read the rest of the content.
Header Tags
Header tags (H1-H6) are HTML elements that separate headings and subheadings from other forms of text in your page (e.g., paragraph text).
Although header tags aren’t as vital for your site’s rankings as they once were, they still serve an important purpose – for both your users and your SEO.
They can have an indirect effect on your rankings by:
- Making it easier and more pleasurable for people to read your information.
- Providing search engines with keyword-rich context about your content.
SEO Writing
SEO writing is creating material that is optimised for both search engines and users.
There’s more to crafting good SEO content than keyword research and filling in the spaces.
Producing content just for the sake of it isn’t going to cut it. Keep in mind that you’re writing content for people, therefore it needs to be of good quality, significant, and relevant.
Keyword Cannibalization
Is this true or false? The more pages you have devoted to a particular keyword, the higher you will rank for that term.
False!
Targeting a single phrase over numerous pages can result in “keyword cannibalism,” which can have severe SEO repercussions. You’re actually competing with yourself if you have many pages ranking for the same keyword.
It’s critical to determine whether keyword cannibalism exists on your website and to address it as soon as possible.
Content Audit
Most content creators are so focused on developing new content that they overlook the need of auditing what they already have. And this is a blunder.
Auditing your current material is important since it allows you to:
- Examine whether your current content is accomplishing its objectives and providing a return on investment.
- Determine whether the information in your material is current or has become outdated (or even outdated).
- Determine which content kinds are most effective for you.
- Content audits are extremely beneficial to your SEO strategy and should be carried out on a regular basis.
Image Optimization
Adding photos to your webpages is a great way to make them more appealing. However, not all photos are made equal, and some can even cause your website to slow down.
By properly optimising photos, you can make the most of a vital SEO tool.
There are numerous advantages to image optimization, including:
- Additional options for ranking (show up on Google Image Search).
- A more pleasant user experience.
- Page load times are faster.
- Images should not be a last-minute consideration. Make sure to utilise meaningful titles and alt text with photos that support your content.
User Engagement
Improving the on-page SEO factors of your website is only half the battle.
The other half is ensuring that users do not bounce, but rather remain to examine your content, interact with it, and return for more.
Retaining engaged consumers is a difficult task in and of itself, but it is possible. Focus on areas such as site performance, user experience, and content optimization, among others, to boost user engagement.
Conclusion
If you want to improve your website’s chances of appearing in search results, on-page SEO is critical. Regularly optimizing for on-site characteristics can help you boost your rankings, visitors, and conversions.
